What are the types of shear failure? According to Vesic (1973) there are three types of shear failures. They are:
- General Shear failure
- Local Shear failure
- Punching Shear failure
These failures are illustrated in Fig 1, 2 and 3.
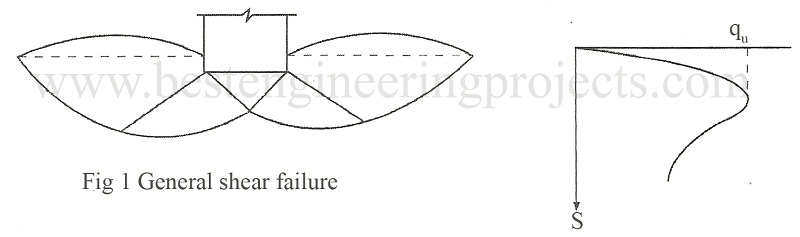
General Shear Failure – This type of failure occurs in stiff clay or dense sand. In this type of failure, failure takes place at a very small strain. The load settlement curve shows a well-defined peak as shown in Fig.1. At failure entire soil mass within the failure wedge participates and well defined rupture surfaces develop. The failure is accompanied by a considerable bulging of sheared mass of soil. There is only marginal difference between the load causing local shear failure and general Shear failure.
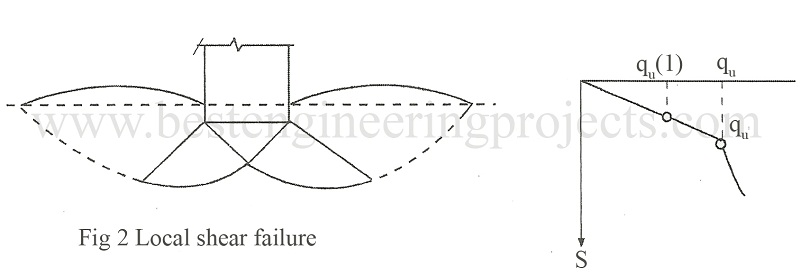
Local Shear Failure – This type of failure occurs in medium dense sand with relative density between 35 – 70 %. In this type of failure, failure takes place at a very large strain. The load settlement curve does not show a well-defined peak as shown in Fig.2. At failure only a small portion of soil underneath the footing participates and well-defined rupture surfaces develop only at points directly below the footing. Bulging of soil at surface begins when strain exceeds about 8 %. The curve shows increase in resistance after failure.
Punching Shear Failure – This type of failure occurs in loose sand or soft clay with relative density less than 35 %. In this type of failure, footing penetrates into the soil without any bulging in the soil at the surface. Increase in vertical load increases the vertical movement and compression in the foundation soil. The failure is accompanied by vertical shear around the perimeter of the footing. At failure, soil outside the loaded area does not participate and there will be no movement of soil on the sides of the footing. This type of failure is shown in Fig.3.
Some Definition
Ultimate Bearing Capacity (Qult) – It is the maximum soil pressure at the base of the foundation which causes shear failure of the supporting soil.
Net Ultimate Bearing Capacity (Qult)net – It is the maximum soil pressure in excess of overburden at the base of the foundation which causes shear failure of the supporting soil.
Safe Bearing Capacity (qs) – It is the safe soil pressure at the base of the foundation which the soil will resist safely without any risk of shear failure irrespective of any settlement that may occur.
Net Safe Bearing Capacity (qns) – It is the safe soil pressure at the base of the foundation in excess of overburden which the soil will resist safely without any risk of shear failure irrespective of any settlement that may occur.
Safe Bearing Pressure (qu) – The intensity of loading that will cause a permissible settlement specified for a given structure.
Allowable Bearing Capacity (qa) – It is the maximum safe soil pressure at the base of the foundation which neither causes shear failure nor produces any settlement in excess of a specified value.

how to do design the circular footing and pile